In a world where traditional classrooms often feel like a never-ending cycle of lectures and homework, alternative education offers a refreshing twist. It’s like swapping a boring salad for a gourmet burger—both can be nourishing, but one definitely packs more flavor. This approach to learning embraces creativity, flexibility, and personalized experiences, making education feel less like a chore and more like an adventure.
Alternative education isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a movement that caters to diverse learning styles and needs. Whether it’s through unschooling, Montessori, or online platforms, the goal is to ignite a passion for knowledge rather than just memorizing facts. So, if you’re curious about what alternative education really means and how it can transform the way we learn, buckle up! It’s time to explore the exciting possibilities that lie beyond the traditional classroom walls.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Alternative Education Meaning
Alternative education represents a broad spectrum of educational approaches that deviate from conventional schooling. It emphasizes personalized learning experiences tailored to individual student needs. Methods such as unschooling, Montessori, and online education platforms fall under this category, each cultivating unique learning environments.
Flexibility characterizes the alternative education framework. Students engage with materials and topics at their own pace, often using real-world applications for learning. This adaptive nature can motivate learners who struggle with the rigid structures of traditional classrooms.
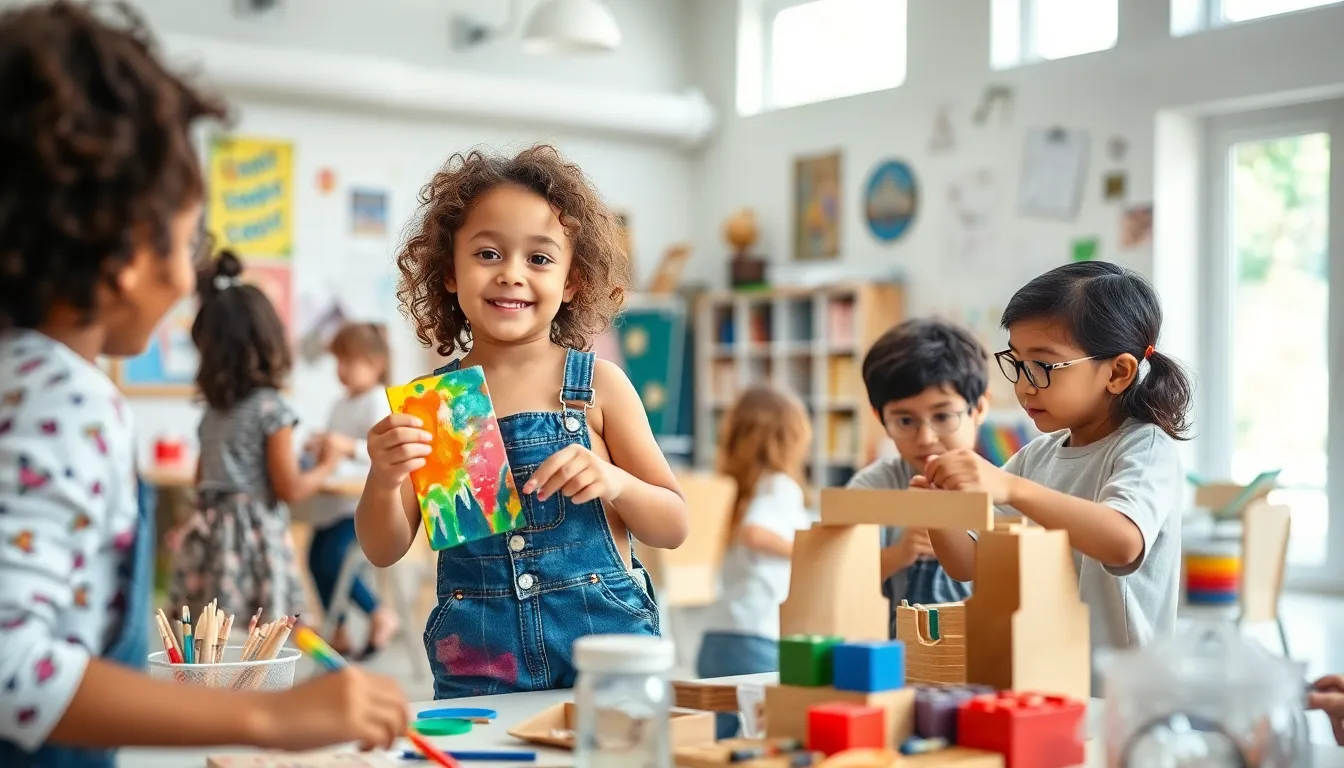
Creative expression plays a significant role in alternative education. Artistic and hands-on projects often take precedence over standardized testing. This creativity fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential in today’s fast-paced world.
Inclusivity is another key aspect of alternative education. Diverse learning styles and backgrounds are embraced, ensuring that all students can thrive. Some alternative schools focus on specific subjects, such as arts or sciences, allowing students to dig deeper into their interests.
Assessment in alternative education differs from standard metrics. Instead of grades, portfolios or progress reports highlight a student’s journey and achievements. This personalized feedback encourages self-reflection and ambition.
Engagement extends beyond academics in alternative education. Community involvement and collaboration enhance the learning experience, allowing students to apply knowledge in meaningful contexts. Through various projects, learners develop a sense of responsibility and connection to their community.
Alternative education prioritizes adaptability, creativity, inclusivity, and engagement. Each of these elements contributes to a holistic learning environment that empowers students beyond traditional educational frameworks.
Historical Context of Alternative Education

Alternative education has roots that stretch back centuries, reflecting diverse approaches to learning. Recognizing the limitations of traditional education, many have sought methods that prioritize individual needs.
Origins and Evolution
Initially, alternative education emerged as a response to rigid schooling systems. In the early 20th century, progressive educators began advocating for student-centered learning. Montessori schools introduced an environment where children could explore at their own pace. Unschooling gained traction in the 1970s, emphasizing freedom in choosing what and how to learn. Over time, alternative education evolved to include blended learning models, incorporating technology and online platforms to enhance engagement.
Key Figures and Movements
John Dewey, a prominent figure in educational reform, championed experiential learning that fosters critical thinking. Maria Montessori’s method focused on self-directed activity and collaborative play. Ivan Illich criticized traditional schooling through his book “Deschooling Society,” promoting a more decentralized approach to education. Waldorf education emerged in the early 20th century, blending artistic activities with academic subjects. Each of these movements contributed unique philosophies that shaped modern alternative education practices.
Types of Alternative Education
Various forms of alternative education exist, each offering unique approaches to learning. These methods prioritize student engagement and personalized experiences.
Montessori Education
Montessori education emphasizes hands-on learning and independence. Children explore various materials at their own pace, promoting self-directed activity. In a Montessori classroom, mixed-age groups foster collaboration and peer-to-peer learning. Educators guide rather than direct, allowing students to take charge of their educational journey. This approach nurtures critical thinking and decision-making skills, essential for lifelong learning. Evidence shows that children in Montessori environments often excel academically and socially compared to their peers in traditional settings.
Waldorf Education
Waldorf education centers on holistic development, integrating arts and academics to enrich the learning experience. Emphasis is placed on imagination and creativity, allowing students to explore subjects deeply. A strong connection to nature is encouraged, with outdoor activities playing a significant role in the curriculum. Teachers in Waldorf schools often remain with the same class for multiple years, fostering strong relationships. This stability enhances trust and encourages emotional growth. Research indicates that Waldorf graduates display strong social and emotional skills alongside academic success.
Unschooling
Unschooling promotes learner-driven education, allowing students to follow their interests without a structured curriculum. Flexibility characterizes this approach, as it prioritizes curiosity and exploration. Parents often facilitate learning by providing resources and support, encouraging their children to seek knowledge in everyday experiences. Unique to unschooling, each learner’s path is tailored, making education relevant to their lives. Many unschooled students develop strong critical thinking skills and a love for learning that persists throughout adulthood. Studies reveal that unschoolers can succeed academically and often thrive in self-directed environments.
Benefits of Alternative Education
Alternative education offers numerous advantages that cater to individual student needs and promote meaningful learning experiences.
Personalized Learning Approaches
Personalized learning approaches in alternative education empower students to pursue knowledge in ways that resonate with them. Learners engage with materials at their own pace, allowing exploration of subjects that spark their interest. Each student’s unique strengths and preferences shape their educational journey. Instead of following a one-size-fits-all curriculum, customization enhances motivation and engagement. Progress isn’t solely assessed through exams; teachers use portfolios and self-reflection methods instead. This individualized focus fosters a deeper connection to the learning process, helping students develop confidence and self-direction.
Fostering Creativity and Critical Thinking
Creativity and critical thinking flourish in alternative education settings. Artistic and hands-on projects frequently replace traditional standardized testing, allowing for diverse expressions of knowledge. Active involvement in real-world applications encourages students to think outside the box. Discussion and collaboration with peers enhance problem-solving skills. Unique learning activities invite innovation and exploration, enabling students to challenge norms and embrace original ideas. Teachers serve as facilitators in this creative environment, guiding students to pursue their interests while developing essential analytical skills. Ultimately, alternative education cultivates a generation of thinkers who thrive in dynamic settings.
Challenges Faced by Alternative Education
Alternative education encounters significant challenges that impact its effectiveness and reach.
Societal Perception and Acceptance
Society often views alternative education with skepticism. Some individuals associate it with inferior academic standards. Misunderstandings about its value can deter families from considering these options. Media portrayals sometimes emphasize failures over successes, fueling misconceptions. Educational institutions may resist change, favoring traditional models that feel familiar. Building awareness and showcasing successes in alternative education is vital for changing perceptions. Highlighting positive outcomes—like increased student engagement and unique learning paths—could foster acceptance and support.
Regulatory and Funding Issues
Navigating regulatory landscapes presents another challenge. Policies for traditional schools often don’t apply to alternative education models. This disparity creates barriers in funding and resources. Schools may struggle to meet state requirements, limiting their operational flexibility. Securing grants and financial support often proves difficult due to inconsistent regulations. Funding shortages can hinder the growth and sustainability of alternative education programs. Advocating for policy changes that support diverse educational models could help secure necessary resources.
Alternative education offers a vibrant alternative to traditional schooling by prioritizing creativity and personalized learning. Its diverse approaches cater to individual needs and encourage students to explore their passions. By fostering critical thinking and real-world applications, alternative education prepares learners for a dynamic future.
Despite facing challenges such as societal skepticism and regulatory hurdles, the benefits of alternative education are undeniable. Emphasizing inclusivity and engagement, it cultivates a generation of innovative thinkers ready to thrive in various environments. As awareness grows, the potential for alternative education to reshape the learning landscape becomes increasingly promising.